Between the surge in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and high-density hardware, businesses are increasingly directing their investments toward edge computing infrastructure. Edge computing’s hallmark is its capability to process data with geographical flexibility, minimizing latency and bandwidth constraints in densely populated computing environments. Recent insights from the Vertiv Edge Survey, predict that 27% of enterprise IT resources will be allocated to the edge, emphasizing the significance of carefully planned and strategic edge AI deployments. However, as densities rise at the edge, the adoption of efficient cooling solutions becomes paramount to fully harness the potential of these high-density devices. In this blog, we discover why enterprises should bring direct-to-chip liquid cooling to the edge to future-proof computing goals.
Percent of IT Resources Deployed in Different Environments Today and in Five years

Figure 1: Vertiv Edge Survey – Percent of IT resources deployed in different environments today and in five years.
1. Deploy AI GPU Clusters at the Edge with Liquid Cooling Solutions
Edge computing, essential for real-time responsiveness, is evolving to meet AI demands with GPU-focused data centers. This shift, highlighted by Jensen Huang, comes with the challenges of managing heat, especially critical in edge AI deployments using dense GPU and CPU clusters. As data volumes inevitably grow, the practicality of transferring it to the cloud diminishes, making investments in specialized GPU hardware for edge AI deployments a logical choice. As reported by Vertiv, 38% of enterprises cite data-intensive workloads such as AI and the Internet of Things (IoT) as their primary motivation for edge computing deployments. This trend highlights the advantages of AI in edge computing and underscores the importance of liquid cooling for operational efficiency.
As power demands continue to rise, traditional air cooling, which is effective for densities up to 10 kilowatts per rack, encounters difficulties with the high TDP GPUs required for high-performance computing (HPC) and AI applications. The increasing prevalence of generative AI has led to rack configurations exceeding 40 kilowatts, driving the adoption of liquid cooling solutions in edge data centers. With the migration of GPUs to the edge, liquid cooling solutions are set to play a pivotal role in providing both power and cooling solutions for edge infrastructure.
Percent of Edge Computing Sites Currently Supporting Edge Use Cases
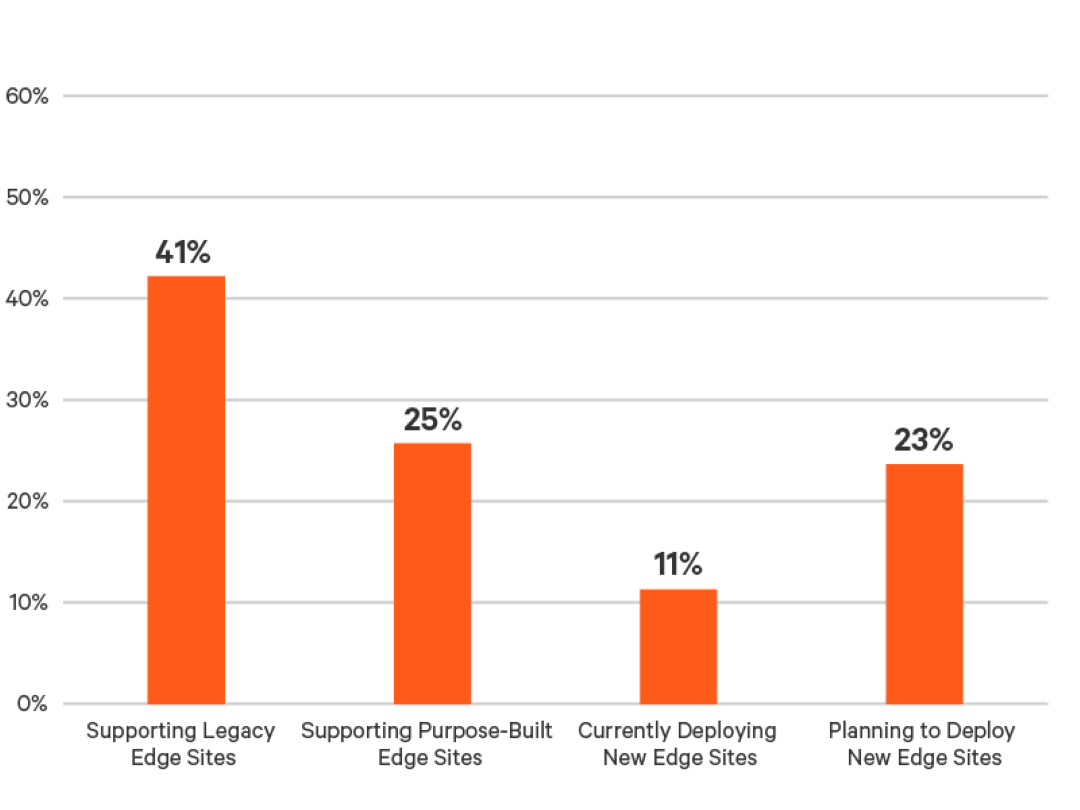
Figure 2: Vertiv Edge Survey – Percent of edge computing sites currently supporting edge use cases (grouped)
2. Maximize Edge Real Estate and Eliminate CDUs
Provisioning efficient data center cooling infrastructure within compact edge computing spaces presents a significant challenge. Traditional liquid cooling solutions that utilize Cooling Distribution Units (CDUs) and their associated infrastructure in edge deployments face space limitations. In response to these constraints, a surge in hybrid liquid-assisted air-cooling solutions that blend air and liquid cooling is accelerating at the edge.
This space-saving liquid-assisted air-cooling solution is particularly advantageous in edge computing environments where real estate is at a premium, allowing for high-performance computing without the spatial constraints of conventional liquid cooling solutions.
3. Provision Scalable Liquid Cooling for Edge Deployments
The AI boom has created a race to enable scalable infrastructure to support AI across diverse data center campuses. However, despite the undeniable advantages of AI, many enterprises are adopting phased approaches to mitigate risk considering the uncertainty and volatility surrounding the AI market. This cautious approach extends to cooling infrastructure, resulting in a demand for iterative, flexible, and scalable liquid cooling solutions at the edge.
In response to this demand, liquid-assisted air-cooling solutions again emerge as a transformative solution since companies can scale as effortlessly as traditional air-cooled servers. With no maintenance for the lifetime of the server, these liquid-assisted systems can truly be a plug-and-play solution that can easily expand in tandem with the growth of edge computing strategies.
4. Increase Power Efficiency and Sustainability
In addition to being a set-it-and-forget-it liquid cooling option, self-contained liquid cooling solutions also drive energy savings, saving up to 100W per server, all without consuming water. Gartner predicts that data centers deploying specialty cooling and density techniques will see 20% to 40% reductions in operating costs by 2025. As we witness AI models, like ChatGPT, “drinking” one 16-ounce water bottle every time you ask it a series of 5 questions, it underscores the importance of efficient cooling in edge AI computing.
5. Peak Performance in Harsh Environments over 35°C
Deploying at the edge not only requires efficient cooling, but also location-agnostic cooling solutions with minimal maintenance. Edge computing is often remotely located and monitored, requiring liquid cooling solutions that are flexible in harsh environments. Specifically, closed-loop, self-contained liquid cooling systems support location-agnostic edge deployments due to their ability to thrive in ambient temperatures above 35°C and last the lifetime of the server. This resilience ensures that AI operations at the edge remain uninterrupted, regardless of external conditions.
Edge AI Applications and Use Cases
Edge computing is revolutionizing various sectors, such as transportation, healthcare, finance, telecommunications, and the development of digital twins. It facilitates real-time monitoring, control, and process optimization, leading to more effective data analysis and decision-making directly at the source.
Transportation: In the transportation sector, edge computing supports autonomous vehicles (AVs) and electric vehicles (EVs). For AVs, edge computing allows for real-time data processing, crucial for immediate decision-making and responsiveness in dynamic driving environments. This enhances safety and efficiency by quickly analyzing sensor data to navigate roads and traffic. In EVs, edge computing supports battery management systems by monitoring and optimizing battery usage and health in real-time. It also enables smarter charging solutions, integrating with smart grids for efficient energy use and distribution.
Healthcare: Edge computing in healthcare revolutionizes remote patient monitoring by enabling real-time data analysis from medical devices. This technology enhances telemedicine by improving the quality of virtual consultations through reduced latency. Additionally, it effectively handles large volumes of data from numerous medical devices, which streamlines workflow efficiency and aids in predictive analytics, crucial for early disease detection and crafting personalized treatment plans.
Finance: In the finance and high-frequency trading (HFT) industries, edge computing plays a pivotal role in significantly reducing latency, a crucial element in the execution of trades. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing effectively minimizes the time delay in receiving and responding to financial data. This accelerated processing capability offers substantial advantages, ultimately translating into cost savings and enhanced profitability for trades.
Digital Twins: Edge computing greatly enhances the development and processing of digital twins, which are virtual replicas of physical systems. By providing real-time data processing at the source, edge computing ensures that the digital twins receive timely and accurate data, crucial for their effectiveness. This immediacy allows for more precise monitoring, analysis, and simulation of the physical counterpart, leading to improved decision-making and operational efficiency.
Telecommunications: Edge computing significantly boosts telecommunications, particularly in the 5G era, by enabling localized data caching. This approach reduces the need to send traffic through often congested central backbone networks. By processing and storing data closer to the end-user, edge computing allows for faster access to content and smoother streaming services. This not only enhances user experience by reducing latency but also alleviates bandwidth pressure on central networks, making 5G networks more efficient and responsive to the increasing demand for high-speed, low-latency communication.
Prepare for Edge AI with D2C Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling at the edge is a vital component in modern edge computing strategies. It addresses the challenges of heat management, space optimization, and energy efficiency, enabling businesses to fully harness the power of AI and IoT at the edge. The rise of direct-to-chip liquid cooling marks a significant advancement in making edge computing more sustainable, efficient, and ready for the demands of future technological innovations.







